The Purpose of MVP
One of the biggest reasons startups fail is because founders design their initial product based on assumptions. As an entrepreneur, you don’t want to put an enormous amount of time, effort and money into a product the market may not even want.
Quibi – yes, that Quibi – is an excellent example of this. After spending upwards of $63 million, Quibi never quite found its footing among TikTok, YouTube and its many streaming competitors. The company never ran an MVP or any experimental public beta to test what kind of content and features resonated well with audiences, and simply built a product that nobody wanted or needed. After raising $1.75 billion in venture capital, the company shut down less than a year after its initial launch. This is why starting with an MVP is so important.
How To Build An MVP
By definition, a minimum viable product is a product with enough features to attract early-adopter customers and validate a product idea early in the development cycle. It allows founders to collect the maximum amount of user feedback with the least amount of effort. When building an MVP, you’ll want to keep the following things in mind:
– Answer the right question. It’s important to determine what your central hypothesis is. When Airbnb’s founders wanted to see if they had a viable idea, they didn’t rent out space or buy new beds. They simply tested the question “Will strangers pay to stay in my apartment?” by providing a free lodging experience in their living room with the promise of networking with like-minded people.
– Decide which metrics matter. Identify what will define the success of your product. Common MVP metrics include churn rate, customer acquisition cost, average revenue per user and lifetime value of a customer. However, the data collected should include both qualitative and quantitative insights about how your product is used and what customers actually think about it.
– Actively measure what you are testing. It is important to continuously test, measure and learn until the product is finalized.
– Build internally if possible. It’s easier to meet internal needs and challenges first. For example, the original Twitter prototype was designed for internal users at (the now closed) Odeo as a way to send messages to other employees and view them on a group level. After initial internal testing and positive feedback, Twitter launched publicly in 2006.
– Do things that don’t scale. In this early stage, you have nothing to lose. Create a great experience for initial users and cater to their needs. Put in the extra amount of effort while you continue to build confidence. Talk with every user and every customer, and do things that would never scale once the company gets bigger. For example, Yelp’s founder Jeremy Stoppelman famously went to every bar in San Francisco to pitch them on Yelp in the early days.
Not Great But Good Enough
When launching Zillow in 2006, we had to decide how good is good enough to launch. The first version of the product had Zestimates on 40 million homes with about a 12% margin of error. When launching, we knew that the Zestimates weren’t going to be entirely accurate and mainly just wanted to see how Americans would react to being able to publicly view valuations and information about homes.
We actually held up the Zillow launch by about two months to avoid angry and upset consumers. We spent this time building out an extra feature called My Estimate that allowed users to modify the estimates of their home with information Zillow didn’t have, such as for things like remodeling or significant changes to square footage. We were worried people might not be happy if the estimate was incorrect and they couldn’t do anything about it, which is why we held off. It was a difficult decision to push back the launch, but worth it in the long run. When striking this balance between our MVP and V1, we knew it didn’t have to be great but just good enough to entice users. Now, 15 years later, Zillow has upwards of 100 million homes with about a 3% margin of error, and the product is much more fully evolved.
Key Takeaway
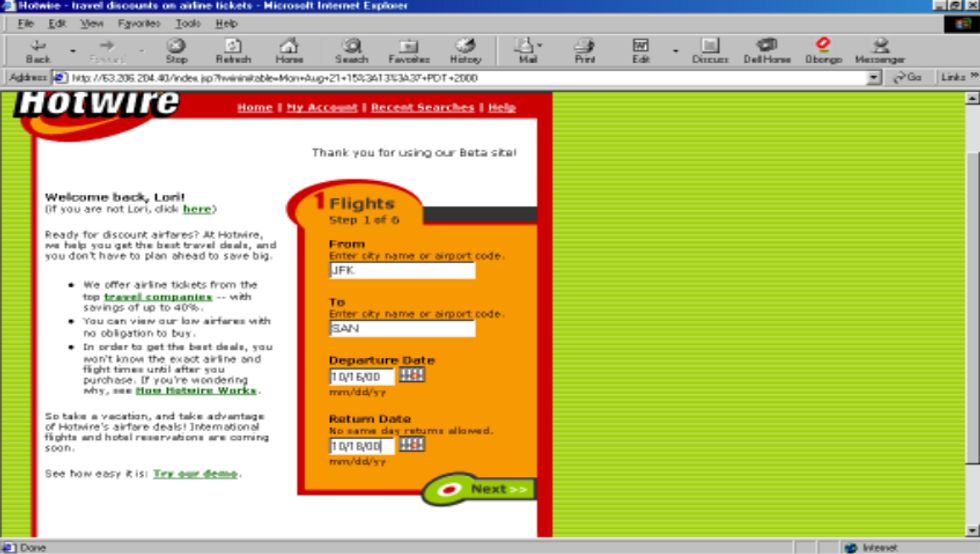
The key takeaway here is that MVP allows organizations to start small, and slowly build up to the best version of their product. When starting Hotwire, we started by just selling airline tickets from a few carriers. Later we expanded to include more airlines, additional flight options, and eventually hotels, rental cars and cruises. But the early MVP was as stripped down as possible. See below for Hotwire’s beta site in 2000. About as bare-bones as it gets.
From Your Site Articles
Related Articles Around the Web
Credit: Source link


Comments are closed.